- PSM is not sufficient for Network and Linux Targets
- Unix, Linux systems are usually critical and are not centrally managed
- Unix Administrators understandably will be reluctant to change their existing workflow and tool set to accommodate a new security layer.
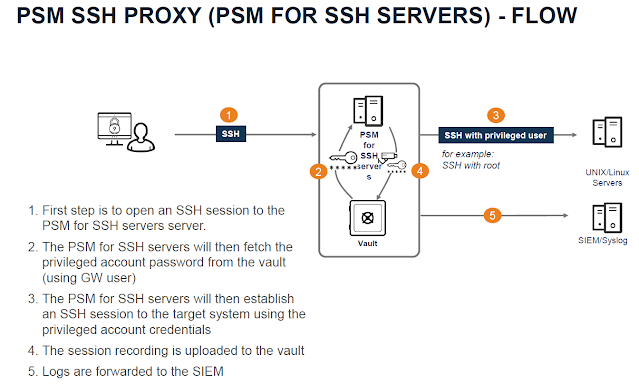
- The solution is to integrate seamlessly with the existing business process, using PSM for SSH Servers.
- The Privileged Session Manager SSH Proxy (PSMP) enables organizations to secure, control and monitor privileged access to network/*NIX devices (only SSH protocol).
- The PSMP is installed on a dedicated machine that has access to the Vault and to the target systems.
Become a Cyberark Certified professional by learning this HKR Cyberark Training!
- Red Hat Enterprise 7.x versions and 8.x versions
- CentOS Linux 7.x and 8.x versions
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 or 12 - 12 SP5
- PSM for SSH can be installed on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platforms
- Quad Core processor (Intel compatible)
- 10 GB disk space for installation, and additional 40GB space for worksapce
- Minimum 8 GB RAM
- 2nd Factor with Radius - Vault must be integrated with Radius Server #Not mandatory
- RedHat Linux v7.0 and above
- CentOs v7.0 and above
- This hardening enforces security best practices recommended for these platforms.
- Copy the PSM for SSH servers software to the server
- Create administrative users on the PSMP machine for future administrative access
- Edit vault.ini file of the installation package to inform the installer where to find the vault on the network
- Create a credential file for the build-in Administrator user for the installer
- Edit PSMPparms file to define the installation path and accept the Software License Agreement
- Install software dependencies and the RPM package
- vi /etc/hosts
- vi /etc/resolv.conf
- vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enxxxx
- Verify configuration
- systemctl restart network
- hostname
- hostname -i
- cat /etc/redhat -release
- ifconfig
- Create administrative user for management task in PSMP ( additional user are specified in the PSMP_MaintenanceUsers parameter in the sshd_config configuration file )
- mkdir /var/PSMP/
- Copy binaries to PSMP directory via WinSCP or SFTP
- chmod -R 777 /var/PSMP/
- Prepare vault.ini
- Create CredFile
- Copy/move PSMP Parameter sample file
- SELinux must be enabled #if its permission or disabled, change it to enforcing and restart the server.
- Install PSMP RPM
- Verify Installation
- Review the following installation log files to ensure the installation completed successfully or find errors that occurred:
- /var/tmp/psmp_install.log : This log file describes the activities that occurred during the installation process
- /var/opt/CARKPSMP/ logs - The following PSMP logs log file describes the activities that occurred when the Vault environment for PSM for SSH servers was created in this directory
- psmpsrv status
- service sshd status
- To repair the PSM for SSH installation, use the following command: rpm -Uvh --force CARKpsmp-version-build number.x86_64.rpm CyberArk PSMP Uninstall: If InstallCyberArkSSHD = Yes or InstallCyberArkSSHD = No Use : rpm –e CARKpsmp If InstallCyberArkSSHD = Integrated rpm –e CARKpsmp rpm –e CARKpsmp CARKpsmp-infra Use the following command to check that PSM for SSH has been uninstalled: rpm –q CARKpsmp
- Run the EnvManager tool in the TeardownEnv mode on the PSMP machine to delete the PSMP environment on the Vault. /opt/CARKpsmp/bin/envmanager "TeardownEnv" -AcceptEULA "Y" -CredFile "/tmp/user.cred" -PSMPAppUser "PSMPAppUser_PSMP1" -PSMPGWUser "PSMPGWUser _PSMP1" Restart the sshd service for these changes to take affect: /etc/init.d/sshd restart
- Impact on Vault
- PSMPADBridgeConf – This Safe contains the main PSMP-ADBridge configuration files used by the PSMP. It is configured to clear history every five days.
- PSMPADBUserProfile – This Safe contains the configuration files that define customized profiles for provisioned users.
- PSMPADBridgeCustom
- PSMPApp_psmp.cyberlab.com - Unique user is created to enable the PSMP to authenticate to the Vault and retrieve passwords.
- PSMPGW_psmp.cyberlab.com - Gateway Account will be used to connect all users to Vault using PSMP
- PSMP_ADB_psmp.cyberlab.com = Group (PSMP_ADB_AppUsers) - A unique user is created to enable the PSMP to integrate with AD Bridge capabilities
- PSMP_ADB_AppUsers
- Impact on Local PSMP server
- Service
- Monitoring the PSM for SSH servers Service
- Monitoring the sshd daemon service
- Configuration Files
- Log files
- PSMPConsole.log contains informational messages and errors that refer to PSM function. This log is meant for the system administrator who needs to monitor the status of the PSM for SSH servers.
- PSMPTrace.log contains errors and trace messages. The types of messages that are included depend on the debug levels specified in the main configuration file.
- Recording Live Session
- ADBridge
- Log Level #if issue comes, then only Work with Cyber-Ark Support
- PVWA = Administration = Options = Privileged Session Management = General Settings = Server Settings = TraceLevels = 1,2,3,4,5
- PVWA = Administration = Options = Privileged Session Management = General Settings =Connection Client Settings = TraceLevels = 1,2
- /opt/CARKPSMP/bin/
- PSM for SSH server
- createenv
- createcredfile
- Changes in the PVWA (Platform and Options)
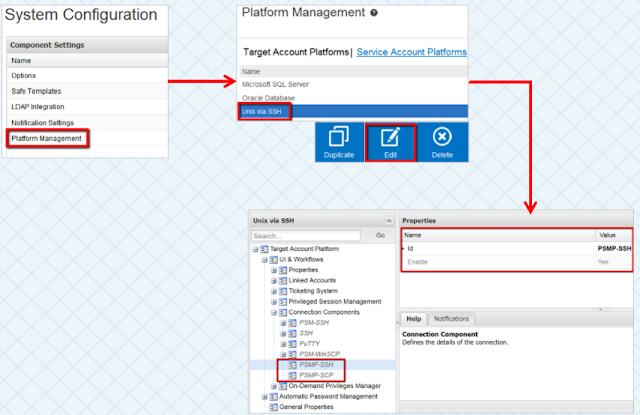
- Assign an AD user to Linux Safe(TestLinuxSafe) with Linux Target server account configured
- Modify the Linux Target Server Platform ( Unix via SSH)
- Verify: UI Workflow = Connection Components = PSMP-SSH = Yes
- PVWA = Administration = Options = Privileged Session Management = General Settings = Server Settings = SSH Proxy Settings
- Testing (Execution of Use Cases)
- After Installation of PSMP, root user will not allow to login, if required login then
- vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- PermitRootLogin Yes
- systemctl restart sshd
- The PSMP is automatically hardened during installation
- Additional manual steps required for harden by Linux administrator
https://linuxize.com/post/how-to-use-linux-sftp-command-to-transfer-files/
The SSH File Transfer Protocol allows you to transfer files from the command line via SSH between a local computer and a specified remote computer. Like SSH, SFTP can be run natively from the shell. This is true of macOS and Linux machines, and is also true of any up-to-date Windows 10 PC