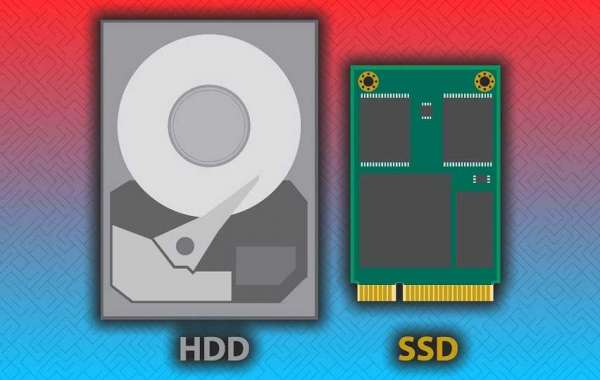
What is an HDD?
The technology behind hard drives is well known and well tested. Hard drives have been around for over 50 years. Hard drives rely on rotating or flat drives to read and write data.
How does work your hard disk drives (HDD)?
Hard drives comprise of at least one attraction touchy platters, an actuator arm with a read/compose head for every platter, and an engine to turn the platters and move the arms. There is likewise an I/O regulator and firmware that guides the equipment and speaks with the remainder of the framework. Each board is organized in concentric circles called tracks. Tracks are divided into logical units called sectors. Every track and number.
Information is kept in touch with the nearest accessible region. There is a calculation that processes information before it is composed, permitting the firmware to distinguish and address blunders. The platters turn at preset rates (4,200 rpm to 7,200 rpm for customer PCs). These speeds are related to read/write speeds. The higher the preset speed, the quicker a hard drive will actually want to peruse and compose information.
Downsides
The disadvantages of hard drives are due to the mechanical parts used to read and write data since searching and retrieving physical data takes longer than finding and retrieving electronic data. Mechanical parts can jump or even fail if roughly handled or fall. This is a concern in laptops, but not so much in desktops. Hard drives are additionally heavier and devour more power than practically identical SSDs.
Writing and Reading
At whatever point you request that your PC recover or refresh information, the I/O regulator tells the actuator arm where the information is and the read/compose head gathers the information by perusing the presence or nonattendance of a heap in each address. Update the data, the read/write head changes the load on the affected track and sector. The time it takes for the platter to turn and the actuator arm to find the right track and sector is called latency.
Advantages of an HDD
The advantages of a hard drive are that it is a proven technology and is often cheaper than an SSD for the same amount of storage space. Currently, hard drives are also available with more storage space than SSDs.
What is an SSD?
SSDs utilize streak memory to give prevalent execution and solidness. Since there are many small moving parts inside the hard drive - magnetic heads, pins, and spinners - it's easy for things to go wrong and you could lose your important data. With no moving parts, IBM 1.92TB SSD is tougher, works at lower temperatures, and burns through less power.
How does Work solid-state drives (SDD)?
SSDs can be thought of as big USB drives; they use the same basic technology. At the lowest level, floating gate transistors register a charge (or no charge) to store data. The doors are organized according to a grid pattern, which is further organized as a block. The size of the block can vary, but each row that makes up the grid is called a page.
Writing and Reading
Updating data is more complex for SSDs. All data in a block must be updated when part of the block is updated. The data from the old block is copied to another block, the block is deleted and the data is overwritten with the change in a new block. Whenever you ask your computer to retrieve or update data, the SSD controller examines the requested data address and reads the state of charge. There is another interaction called TRIM which illuminates the SSD that it can skip modifying a few information when it eradicates blocks.
Since there is a limited number of occasions a square can be overwritten, this is a significant cycle that forestalls untimely wear and tears on the capacity drive. To prevent further wear and tear on the disk, there is an algorithm to ensure that each block on the disk receives an equal amount of read/write process. This process is called wear leveling and occurs automatically while the unit is in operation.
The writing process requires moving data, SSDs usually have over-provisioned storage; there is always a certain amount of the drive that is not reported to the operating system and is not accessible to the user. This allows the driver to move and delete items without affecting the overall storage capacity.
Disadvantages
Although they are catching up, it can be more difficult to find large-capacity SSDs. Hard drives can be up to 2.5 times larger.
Is an SSD a hard drive?
Simply put, an SSD is not the same as a hard drive. Hard drives use magnetism-sensitive platters that are moved by a motor, while an SSD uses flash memory with no moving parts, which means they're faster.
Benefits of an SSD
SSDs consume less power, which allows computers to run cooler. One of the biggest advantages of an SSD is that it is much faster than hard drives. For example, Crucial P5 is our fastest NVMe SSD, delivering impressive read / write speeds of up to 3400/3000 MB / s. Portable SSDs are also faster than hard drives. With read speeds of up to 1050MB / s1 and capacities up to 2TB, the X8 is up to 100 times faster than USB2 drives and up to 7.5 times faster than hard drives traditional.